=Overview
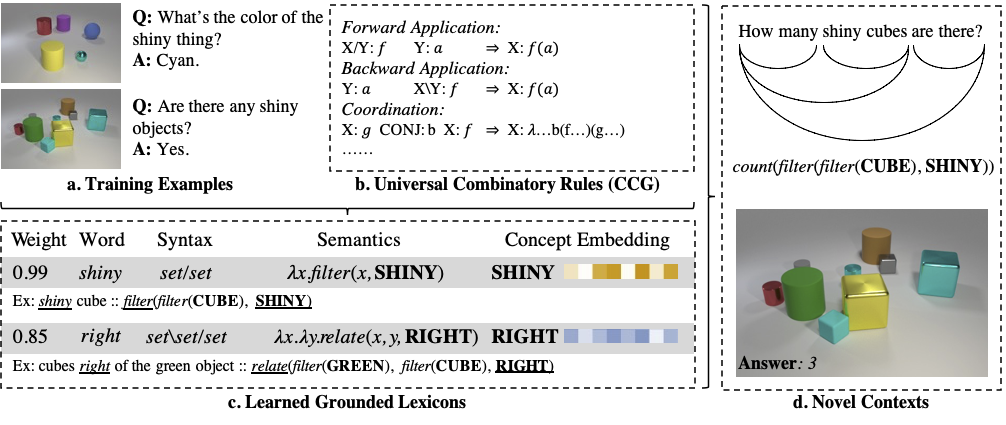
Figure 1: Our framework, Grammar-Based Lexicon Learning (G2L2) learns from grounded language data, for example, by looking at images and reading parallel question–answer pairs. It learns a collection of grounded lexicon entries comprised of weights, syntax types, semantics forms, and optionally, grounded embeddings associated with semantic concepts. These lexicon entries can be used to parse questions into programs.
Abstract: We present Grammar-Based Grounded Language Learning (G2L2), a lexicalist approach toward learning a compositional and grounded meaning representation of language from grounded data, such as paired images and texts. At the core of G2L2 is a collection of lexicon entries, which map each word to a tuple of a syntactic type and a neuro-symbolic semantic program. For example, the word shiny has a syntactic type of adjective; its neuro-symbolic semantic program has the symbolic form lambda x. filter(x, SHINY), where the concept SHINY is associated with a neural network embedding, which will be used to classify shiny objects. Given an input sentence, G2L2 first looks up the lexicon entries associated with each token. It then derives the meaning of the sentence as an executable neuro-symbolic program by composing lexical meanings based on syntax. The recovered meaning programs can be executed on grounded inputs. To facilitate learning in an exponentially-growing compositional space, we introduce a joint parsing and expected execution algorithm, which does local marginalization over derivations to reduce the training time. We evaluate G2L2 on two domains: visual reasoning and language-driven navigation. Results show that G2L2 can generalize from small amounts of data to novel compositions of words.
=Resources
=Related Publications
The Neuro-Symbolic Concept Learner: Interpreting Scenes, Words, and Sentences From Natural Supervision
- ICLR 2019 (Oral)
- Paper /
- Project Page /
- BibTeX
Neural-Symbolic VQA: Disentangling Reasoning from Vision and Language Understanding
- NeurIPS 2018 (Spotlight)
- Paper /
- Project Page /
- BibTeX